What is an element, compound and a mixture?

Element
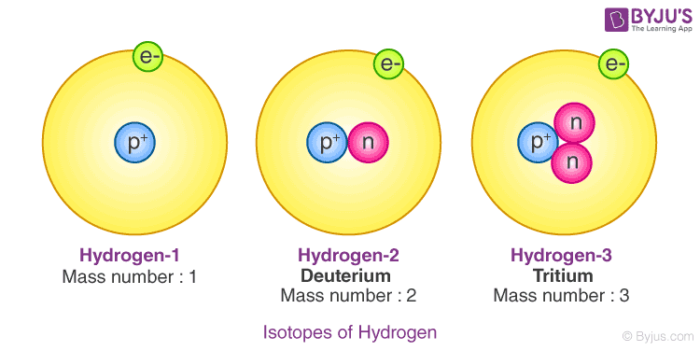
An element is a substance made of only one type of atom. Examples include Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Helium, Silver, Gold, e.t.c.

Compound
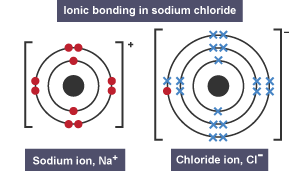
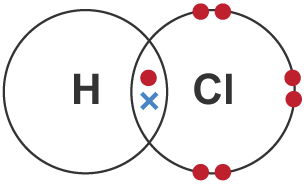
A compound is a substance made of two or more types of atom chemically bonded together. It is commonly named with the metal first and if there's 2 elements, the compound ending has an 'ite'. If there is 3 or more elements and one of them is oxygen, the compound's name will end in 'ate'.
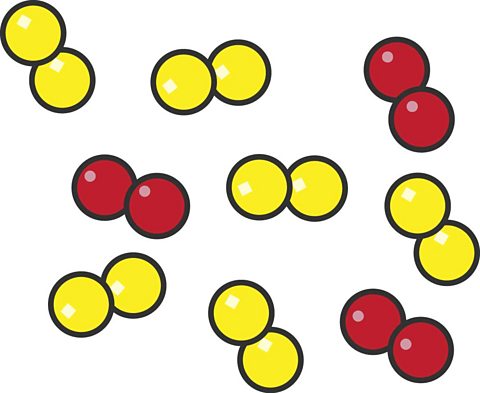
Mixture
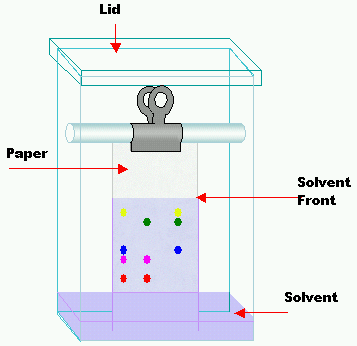
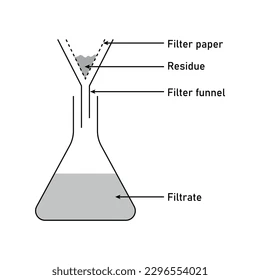
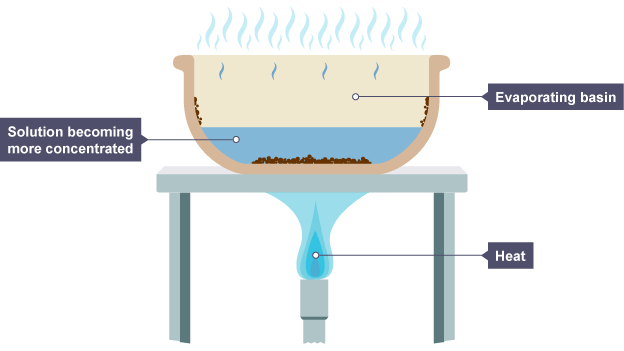
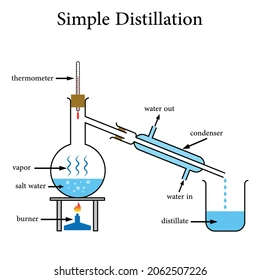
A mixture is a substance made up of two or more different elements or compounds that are physically combined, not chemically bonded.